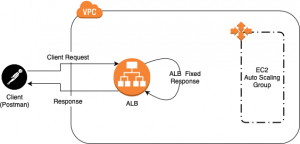
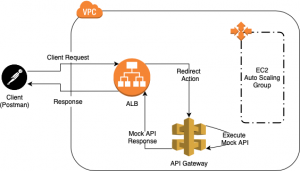
Are you looking to distinguish yourself from other candidates applying for a Software Engineering position? If that’s the case, this blog will guide you in becoming that standout individual.
Software engineering encompasses a diverse range of areas, necessitating fundamental engineering skills for every individual. Furthermore, in today’s era, possessing practical expertise in cloud infrastructure is an essential asset for engineers aiming to excel in the information technology field. In this blog post, our focus will primarily be on exploring Nine vital AWS services that you should adeptly command, ensuring your prominence in the competitive landscape of the IT industry.
AWS Products
How many services and products does AWS offer within its cloud? As of August 2023, the count stands at approximately 239. Can you achieve mastery over all of them? Certainly, but is it a necessity? The answer is mostly no.
Now, let’s delve into the exploration of the Nine essential services you should aim to master in order to flourish on your engineering journey.
Identity & Access Management (IAM) 
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a web service that helps you securely control access to AWS resources. With IAM, you can centrally manage permissions that control which AWS resources users can access.
Key Concepts to Master
- Understanding IAM and its role in managing user access.
- Creating users, groups, and roles.
- Setting permissions and policies.
Video –> AWS IAM Core Concepts You NEED to Know
Basic Networking Concepts in AWS (VPC) 
Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC), you can launch AWS resources in a logically isolated virtual network that you’ve defined. This virtual network closely resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center, with the benefits of using the scalable infrastructure of AWS.
Key Concepts to Master
- Overview of Amazon VPC (Virtual Private Cloud)
- A VPC is a virtual network that closely resembles a traditional network that you’d operate in your own data center. After you create a VPC, you can add subnets.
- AWS Regions are physical locations around the world where Amazon clusters data centers for application and service delivery in AWS Availability Zones.
- An Availability Zone (AZ) is a grouping of one or more discrete data centers that provide applications and services in an AWS region.
- Subnets, route tables, and security groups
- A subnet is a range of IP addresses in your VPC. A subnet must reside in a single Availability Zone. After you add subnets, you can deploy AWS resources in your VPC.
- Public & Private Subnet
- Use route tables to determine where network traffic from your subnet or gateway is directed.
- A security group acts as a firewall that controls the traffic allowed to and from the resources in your virtual private cloud (VPC). You can choose the ports and protocols to allow for inbound traffic and for outbound traffic.
Video –> AWS Networking Fundamentals
Deploy your services in EC2 
Amazon EC2 provides scalable computing capacity in the AWS cloud. Leveraging it enables organizations to develop and deploy applications faster.
Key Concepts to Master
- Launching, configuring, and connecting to EC2 instances.
- A security group acts as a virtual firewall for your EC2 instances to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Inbound rules control the incoming traffic to your instance.
- Outbound rules control the outgoing traffic from your instance.
- Overview of instance types, storage options
- Instance type that you specify determines the hardware of the host computer used for your instance. Each instance type offers different compute, memory, and storage capabilities, and is grouped in an instance family based on these capabilities.
- Data Storage for the EC2 instances ranging from EBS and EFS
- Elastic Loadbalancer
- Elastic Load Balancing automatically distributes your incoming traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses, in one or more Availability Zones.
Video –> Launch an AWS EC2 Instance Tutorial
Container Orchestration via Amazon ECS 
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a fully managed container orchestration service that simplifies your deployment, management, and scaling of containerized applications. This service helps you to run your applications or services in docker containers.
Key Concepts to Master
- Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) is a fully managed container registry offering high-performance hosting, so you can reliably deploy application images and artifacts anywhere.
- Cluster – Logical group of container instances
- Container Instance – EC2 instance in which ECS agents runs and is registered to cluster.
- Task Definition – Description of application to be deployed
- Task – An instantiation of task definition running on container instance
- Service – Runs and maintains predefined tasks simultaneously
- Container – Docker Container created during task instantiation
- ECS launch type – EC2 and Fargate
Video –> Deploy an Application to Amazon ECS With EC2 | Docker | ECR | Fargate | Load balancer
Serverless computing with AWS Lambda 
AWS Lambda is a serverless, event-driven compute service that lets you run code for virtually any type of application or backend service without provisioning or managing servers.
Key Concepts to Master
- Writing and deploying serverless functions
- Serverless framework is a very good tool to deploy serverless applications
- Event triggers and integration with other AWS services.
Video –> How to Deploy AWS Lambda using Serverless Framework
Object Storage 
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service offering industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance. Most of the time S3 is been used to store static content of you web application frontend.
Key Concepts to Master
- Understanding object storage and the basics of S3 buckets.
- Amazon S3 to host a static website. On a static website, individual webpages include static content. They might also contain client-side scripts.
- Deeply couple with AWS Cloudfront for content delivery
- Uploading, downloading, and managing objects in S3.
- Object versioning
- Overview of data durability, availability, and access control.
- Public Access
- Private Bucket & Bucket Policy
Video –> Secure Static Hosting with S3, CloudFront and OAI
Database or AWS fully managed Relational Database (RDS) 
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a collection of managed services that makes it simple to set up, operate, and scale databases in the cloud. Choose from seven popular engines — Amazon Aurora with MySQL compatibility, Amazon Aurora with PostgreSQL compatibility, MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQL Server.
Key Concepts to Master
- Creating and configuring RDS instances.
- Select the Database engine and Size of the instance
- Connecting applications to RDS databases.
- Security group configuration and port configuration
- RDS Cluster (Reader & Writer Instances and Endpoints)
Video –> AWS RDS MySQL Database Setup | Step by Step Tutorial
Monitor & Access Your Application Logs via CloudWatch 
Amazon CloudWatch collects and visualizes real-time logs, metrics, and event data in automated dashboards to streamline your infrastructure and application maintenance. Must have tool to troubleshoot and debug your application issues.
Key Concepts to Master
- Application Logs
- Log Groups which collect the service logs
- Log Insights to query logs
- Setting up alarms and notifications.
- Setup infrastructure alarms
- Create monitoring dashboards
- Define rules to trigger events (Lambda functions)
- Using AWS CloudTrail for auditing and tracking API activity.
- To monitor AWS service level access
Video –> AWS Cloudwatch Service Overview | Console Walkthrough
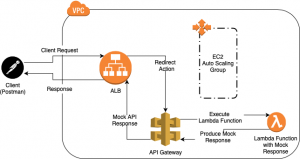
By delving deeper into the services and their key features mentioned above, you can acquire the necessary skills to advance in your software engineering journey. Given below is a sample architecture diagram where you have the services we mentioned and some more additional ones.
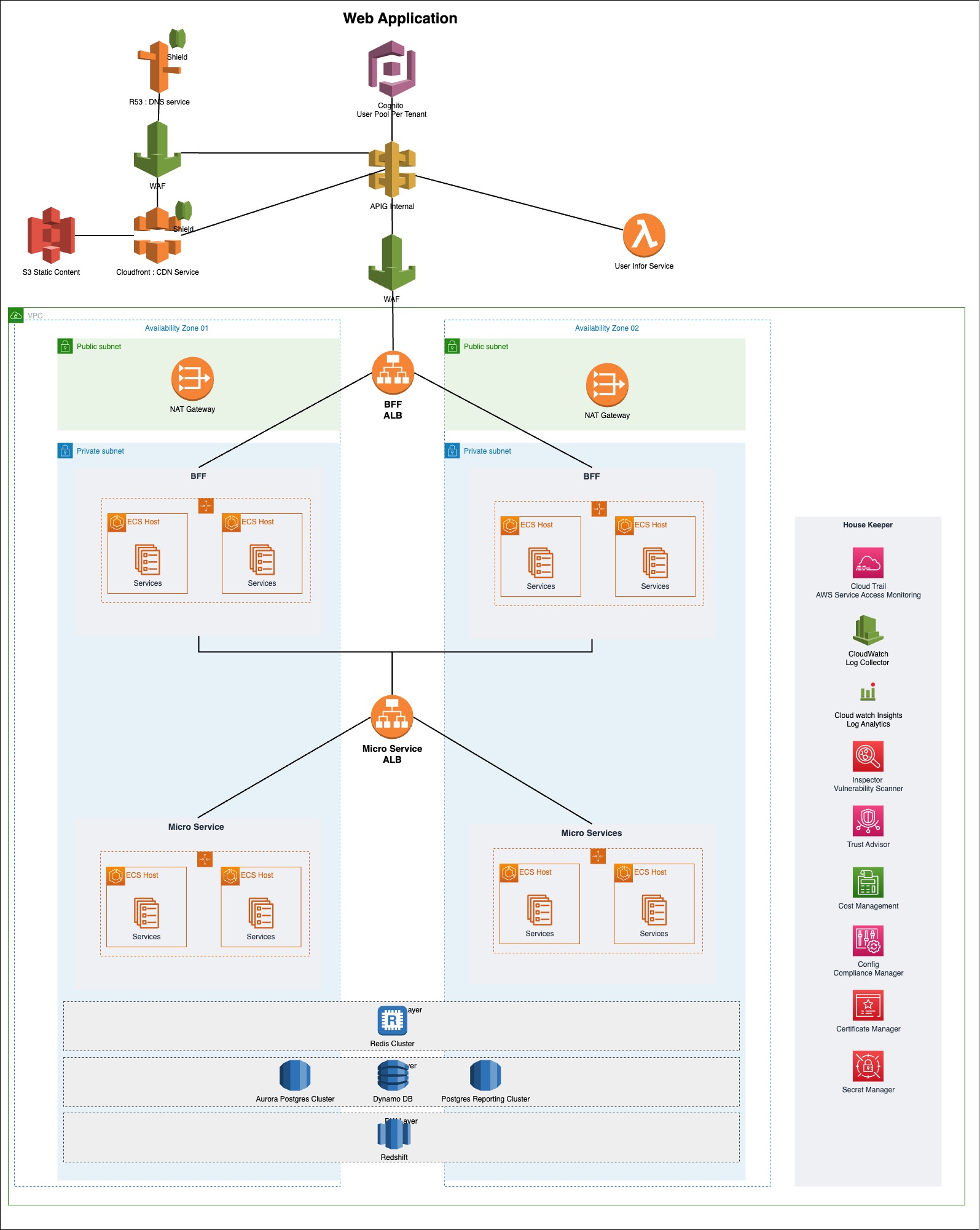
Below, you’ll find valuable links to help you study these services extensively. I hope these resources assist you in mastering AWS services and transforming into an AWS Ninja within your organization.
- AWS Networking Fundamentals
- AWS IAM Core Concepts You NEED to Know
- Secure Static Hosting with S3, CloudFront and OAI
- Launch an AWS EC2 Instance Tutorial
- Deploy an Application to Amazon ECS With EC2 | Docker | ECR | Fargate | Load balancer
- How to Deploy AWS Lambda using Serverless Framework
- AWS RDS MySQL Database Setup | Step by Step Tutorial
- AWS Cloudwatch Service Overview | Console Walkthrough
- Intro to AWS – The Most Important Services To Learn