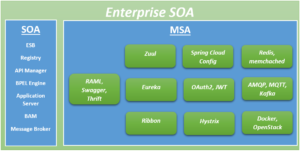
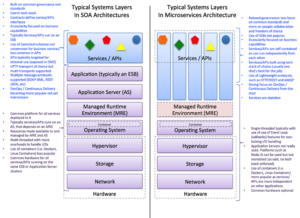
In previous posts we discussed on different topics of Service Oriented Architecture and Microservices. In this post we will discuss how Microservices moving in to the traditional SOA solutions.
In software engineering, SDLC (System Development Life Cycle) is a well know process. Similarly when we want to develop SOA solutions, there is similar process which is illustrated in the below diagram.
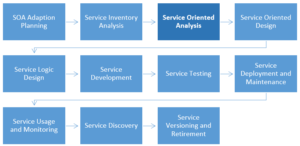
In the Service Oriented Analysis and Design stages, microservices comes in to the picture. Before we proceed let’s get a quick introduction to microservices. In SOA world microservice represent a specific performance / reliability requirement (business process) in a SOA solution. Its holds a distinct implementation environment optimized to support special processing demands that required for performance and reliability needs. Microservice is an independent service, however when a microservice needs to access other resources (services), those resources can either be replicated or redundantly implemented so that they remain part of the microservice’s local processing scope. Therefore, when it is decided that a microservice needs to compose another service, the composed service may be redundantly implemented and deployed together with the microservice.
Service Analysis and Modeling Process
Now let’s check how microservices are produced in a SOA solution on a given Business Process.
Step 1 | Analysis of the Business Process:
Main goal of this step is to decompose the business process to smaller processors. To achieve this we can follow the below steps
- Identify main processors in the business process
- Breakdown each main process in to small processes
- Draw the detail business process flow diagram
- Identify small processes which cannot be automated or should not be automated. Those processes should only handle through a manual process. So remove them from the list of process which are candidates for service implementation
Step 2 | Define Entity Services:
From the list of processes which are candidates’ service implementation, find out reusable agnostic services candidates and its capabilities. Those services can be categorized as entity services.
Step 3 | Define Task Services:
These are the services which has process specific logic (non-agnostic). After identifying the entity services, the remaining can be categorized under task service. Normally we can find business rules, conditional logic which is specific to a process in this kind of services.
Step 4 | Apply Service Orientation:
Revisit the services which we have categorized and try to apply service orientation principles on them. Service loose coupling, Service abstraction and Service autonomy to those services.
Step 5 | Identify Service Composition Candidates:
In this step, we will look at the entity and task services that we captured during earlier stages and check whether those are candidates for service compositions.
Step 6 | Analyze the processing requirements:
For each process / sub process we need to follow the following steps to identify special requirements
- What are the processing logic required in each service
- Did we identified them earlier or do we need to redevelop them
- What are the external resources we need to access via our services (DB, Message Brokers, Legacy systems)
- Any logic critical for performance and reliability
- This is the point where need of microservices comes in to picture in SOA solution
- By producing performance and reliability critical services as microservices, we can ensure other services won’t have any impact from those performance critical services. Since those are run independently
Step 7 | Define Utility Services:
From the agnostic processing logic which we identified earlier, check if there are any reusable utility services. For example logging services and notification services.
Step 8 | Define microservices candidates:
Revisit the non-agnostic process logic which we identified earlier and determine any of the logic can be represent as microservices. Ideal candidate for a microservice would be
- Volatile requirement
- Performance requirement
- Runtime reliability and failover requirement
- Service visioning and deployment requirement
Step 9 | Apply service orientation:
As we did in the step four, repeat the same process to utility and microservices which we identified earlier
Step 10 | Revisit the service composition candidates:
Check whether we can use the microservices and utility services for other service requirements
That’s pretty much it, on the process of analysis and design stage of services in a SOA solution. So we can clearly see where the microservices coming in to play in the SOA solution development process.
References
Read More